Critical Lubrication Points for Steel Mills
Steel mills operate under some of the most demanding conditions, with high temperatures, heavy loads, and continuous operation. The efficiency and reliability of these mills are significantly dependent on the proper lubrication of critical components. In this article, we will explore the essential lubrication points in steel mills, covering key processes such as sponge iron production, kilns, continuous casting, and rolling mills.
Sponge Iron Processes
The production of sponge iron, a primary raw material in steelmaking, involves the reduction of iron ore in rotary kilns or other types of reactors. These processes require the following critical lubrication points:
- Kiln Drive Gears: Lubricating these gears is vital to prevent metal-to-metal contact and ensure smooth operation. Synthetic lubricants with high thermal stability are often recommended for this application. The large gear drives used to rotate the kiln require lubricants with excellent load-carrying capacity and resistance to thermal degradation. Consistent lubrication reduces the risk of gear failure and extends the life of the equipment.
- Sealing Systems: The seals used to prevent dust and gas leakage from the kiln must be lubricated to prevent wear and tear. This helps maintain the kiln's efficiency and reduce maintenance costs.
- Support Roller Bearings: The rollers that support the kiln must be lubricated with high-performance greases capable of resisting contamination from dust and debris. This lubrication helps in maintaining the alignment and stability of the kiln during operation.
- Kiln Tyre Chair Pad: Proper maintenance and installation of Kiln Tyre Chair Pads are essential for the efficient and safe operation of rotary kilns. If the chair pads are worn out or improperly installed, it can lead to uneven tyre wear, misalignment, increased friction, and even structural damage to the kiln, resulting in costly repairs and downtime.
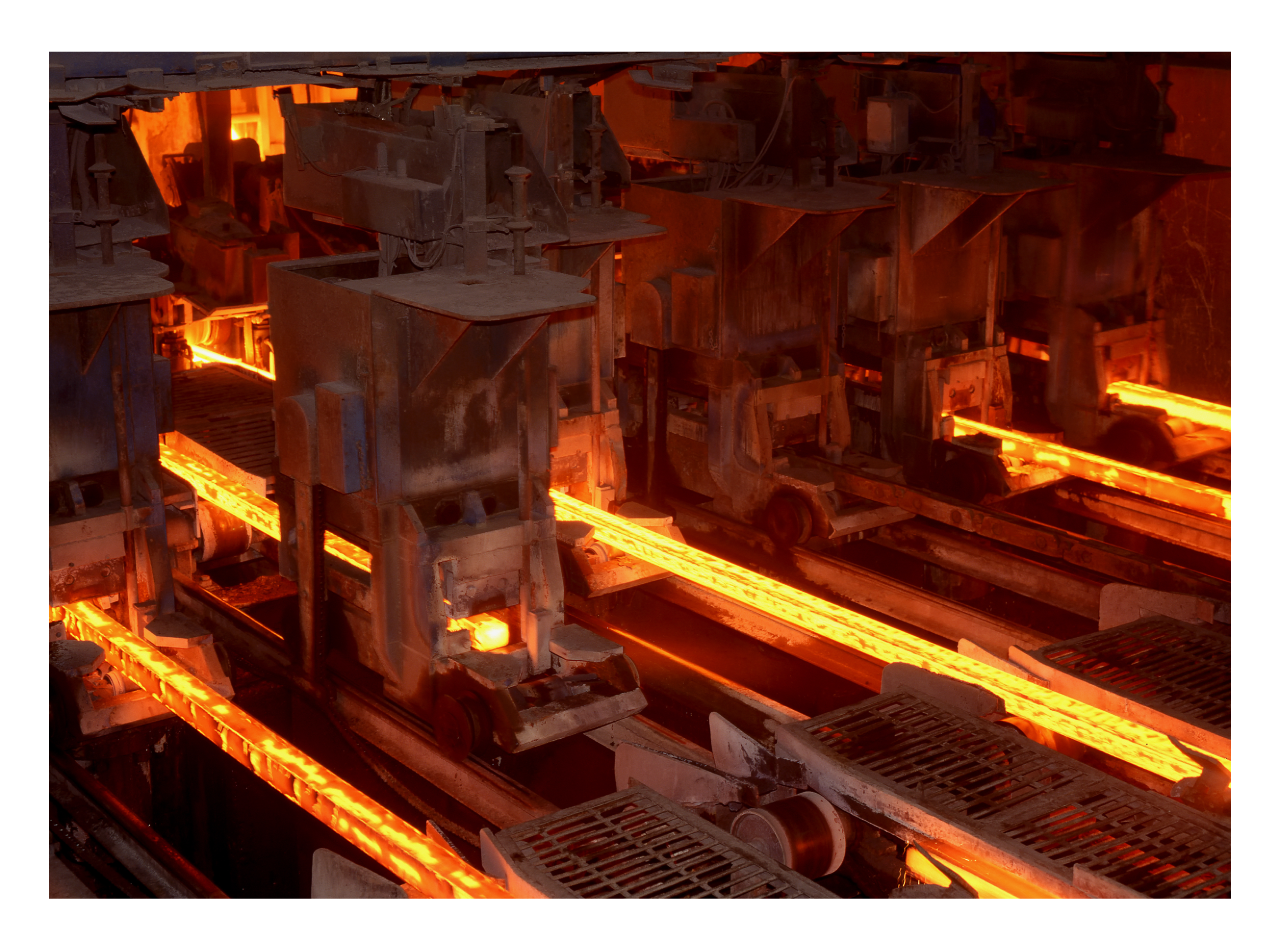
Continuous Casting
In the continuous casting process, molten steel is solidified into billets, blooms, or slabs. This process demands precise lubrication at various stages to ensure high-quality output:
- Mold Lubrication: The mold used in continuous casting must be lubricated with specialized oils or powders to prevent the steel from sticking to the mold walls. This lubrication is critical for achieving a smooth surface finish on the cast product.
- Support Roller Bearings: The rollers guiding the cast steel through the cooling zone require lubrication to handle high temperatures and heavy loads. Proper lubrication here minimizes the risk of roller seizure and ensures consistent product quality.
- Withdrawal and Straightening Units:These units must be lubricated with greases that can withstand both high temperatures and the presence of cooling water. Effective lubrication reduces the risk of breakdowns and increases the lifespan of the equipment.

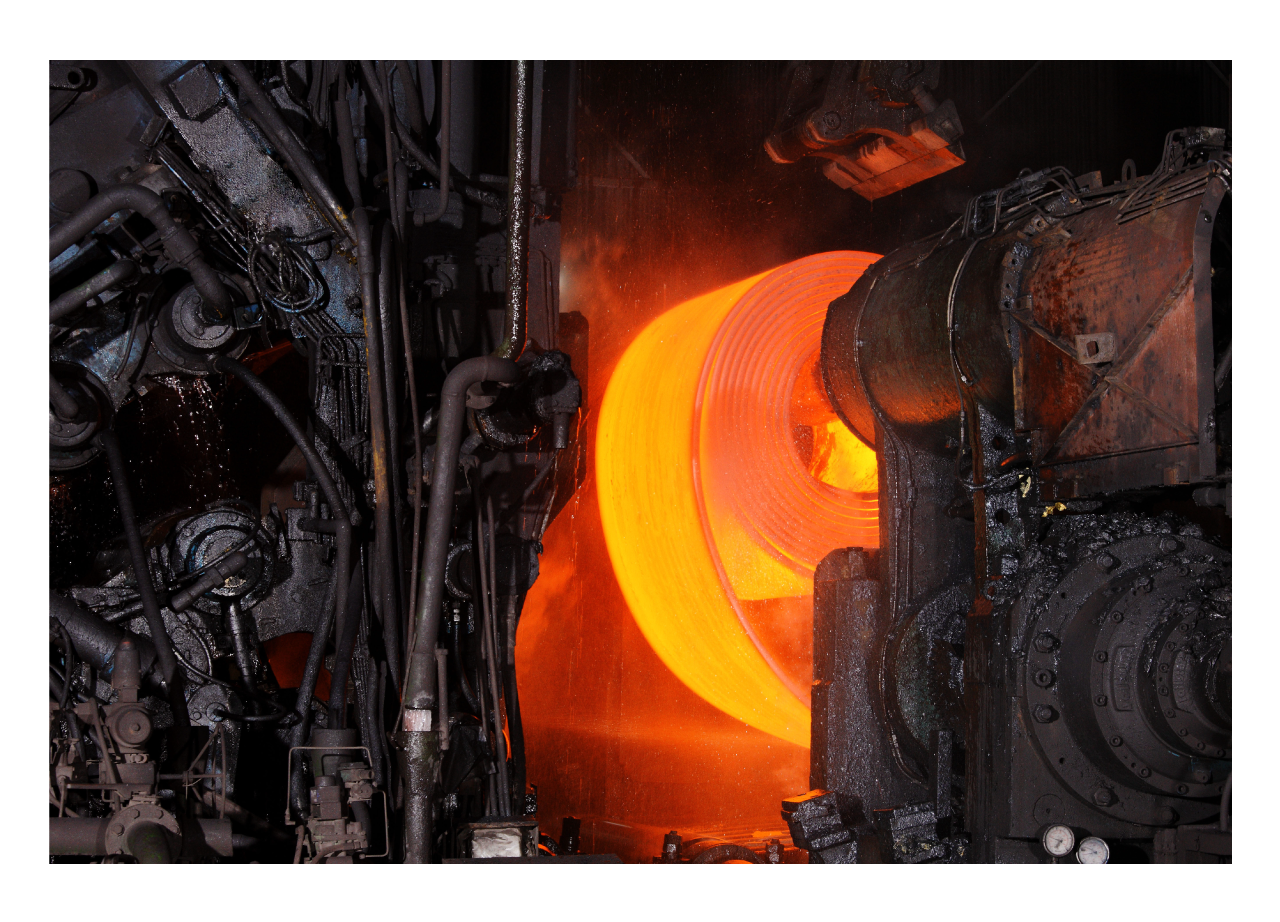
Rolling Mills
Rolling mills are used to reduce the thickness of steel slabs, billets, or blooms through a series of rolling stands. The critical lubrication points in rolling mills include:
- Work Roll & Backup Roll Bearings:These bearings operate under extreme loads and must be lubricated with high-performance greases that can provide adequate protection against wear and corrosion.
- Gearboxes:The gearboxes driving the rolling stands require lubricants with high viscosity and excellent load-carrying capacity. Regular monitoring and maintenance of gearbox lubrication are essential to prevent downtime.
- Hydraulic Systems: The hydraulic systems controlling the rolling mill's operations need clean, high-quality hydraulic fluids to ensure smooth and precise movement. Contaminants in the fluid can lead to system failures and costly repairs.

Maintenance Optimization and Sustainability
While the primary focus of lubrication in steel mills is to reduce friction and wear, optimizing maintenance practices and adopting sustainable lubrication solutions can yield significant long-term benefits.
- Condition Monitoring: Implementing condition monitoring techniques, such as vibration analysis and lubricant analysis, can help identify potential issues before they lead to equipment failure. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and extends equipment life.
- Sustainability:With increasing emphasis on sustainability, steel mills are encouraged to adopt environmentally friendly lubricants that reduce the environmental impact without compromising performance. Biodegradable and synthetic lubricants offer excellent protection while being less harmful to the environment.
- Automated Lubrication Systems: These systems ensure consistent and precise lubricant application, reducing the risk of over- or under-lubrication. They also minimize waste and reduce manual labour, contributing to overall operational efficiency.
Effective lubrication is critical to the efficient operation of steel mills. By focusing on the key lubrication points in sponge iron processes, kilns, continuous casting, and rolling mills, operators can significantly reduce maintenance costs, improve equipment reliability, and enhance overall productivity. Utilizing the right lubricants for each application, along with regular monitoring and maintenance, is essential to achieving these goals.
About the Author
Samarth is a highly skilled individual with qualifications in
Law and Business Management. However, his true passion lies in
expanding the reach of Molygraph Lubricants on a global scale. He has
played a pivotal role in leading international business teams and
marketing teams and has successfully established a wide network of
channel partners across the world. Contact Mr. Samarth Shah at
samarth@molygraph.com
Mr. Samarth Shah
Director | Molygraph Lubricants


